Mountain biking offers exhilarating challenges and breathtaking adventures through rugged terrains. To conquer obstacles with ease and elevate your performance, it’s crucial to unlock the full potential of your mountain bike’s gear system. In this article, we’ll guide you through the art of using gears on a mountain bike, enhancing your riding experience, improving efficiency, and tackling difficult terrains effortlessly.
Introduction
What is a mountain bike?
A mountain bike is a specialized bicycle designed for off-road riding on rough terrains. It features sturdy frames, wide knobby tires, and a suspension system to absorb shocks. Mountain bikes are equipped with multiple gears, allowing riders to navigate steep climbs, descend smoothly, and maintain speed on flat terrain.

Average Prices
showcasing the average price range of Gears on a Mountain Bike:
| Gear Component | Price Range (USD) |
| Front Derailleur | $20 – $100 |
| Rear Derailleur | $40 – $200 |
| Shifters | $50 – $300 |
| Chain | $10 – $60 |
| Cassette | $50 – $300 |
| Chainrings | $20 – $150 |
| Bottom Bracket | $20 – $100 |
| Crankset | $50 – $400 |
Types of Gears
Different types of Gears on a Mountain Bike commonly found in mountain bikes:
| Gear Type | Description |
| Single Speed | A single gear ratio, usually used for simplicity and durability |
| Double Chainring | Two front chainrings, providing a wider range of gear ratios |
| Triple Chainring | Three front chainrings, offering an even wider range of gear ratios |
| Cassette | A cluster of rear cogs, providing multiple gear options |
| 10-Speed | A 10-speed cassette, offering 10 different gear ratios |
| 11-Speed | An 11-speed cassette, providing 11 gear ratios |
| 12-Speed | A 12-speed cassette, offering 12 gear ratios |
| Internal Gear Hub | A sealed gear system located within the rear hub, providing gear options without external derailleurs |
| Gear Ratio | The ratio between the number of teeth on the chainring and the rear cog, determining the ease or difficulty of pedaling |
Importance of Gears on a Mountain Bike
Gears play a crucial role in mountain biking by allowing riders to adapt to different terrains and riding conditions. They provide a range of gear ratios, enabling cyclists to exert the appropriate amount of power for efficient pedaling. Gears make it easier to tackle steep climbs, conserve energy, and maintain a comfortable cadence.
Understanding Gears on a Mountain Bike
To effectively utilize gears on a mountain bike, it is essential to understand the gear system’s functioning and its various components.
Explanation of the gear system
A Gears on a Mountain Bike system consists of two primary components: the front derailleur and the rear derailleur. The front derailleur controls the movement of the chain between the front chainrings, while the rear derailleur facilitates shifting between the cassette’s rear cogs.
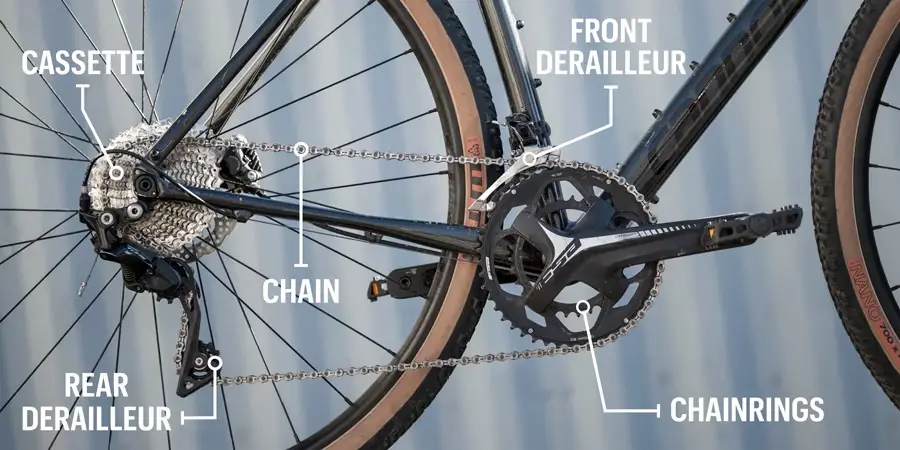
The chainrings and cogs are the toothed rings located at the front and rear wheels, respectively. The number of teeth on these rings determines the gear ratio and the ease or difficulty of pedaling.
Gear Shifting Techniques
Mastering the art of shifting Gears on a Mountain Bike smoothly is crucial for a seamless riding experience. Here are some key techniques to keep in mind:
Basic gear-shifting principles
When shifting gears, it is important to maintain a steady pedaling cadence and avoid excessive force on the pedals. Shift one gear at a time, allowing the chain to smoothly transition from one cog to another. Anticipate terrain changes and shift preemptively to maintain an optimal gear ratio.
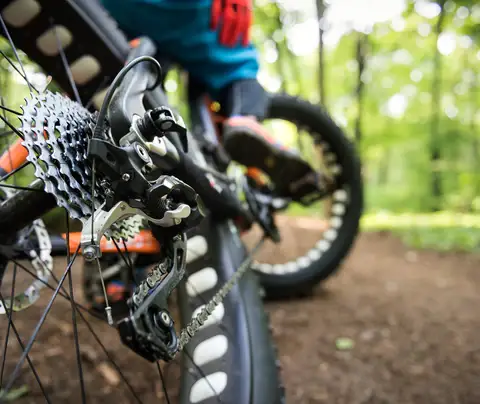

Shifting gears smoothly
To shift gears smoothly, release pressure on the pedals momentarily while shifting. Use your thumb and index
finger to operate the gear shifters, keeping a firm grip on the handlebars. Practice shifting gears while riding on flat terrain before tackling more challenging trails.
Understanding gear ratios
Gear ratios determine the mechanical advantage and the difficulty of pedaling. Lower gears provide easier pedaling for uphill climbs, while higher gears offer more speed on flat terrain or downhill descents. Experiment with different gear combinations to find the most comfortable and efficient ratios for different riding conditions.
Using Gears for Climbing Uphill
Climbing uphill on a mountain bike requires the right gear selection and efficient pedaling techniques. Here’s how to conquer uphill climbs effectively by Gears on a Mountain Bike:
Choosing the right gear for climbing
When approaching an uphill section, shift to a lower gear to reduce the pedaling effort. Lower gears make it easier to maintain a steady cadence and conquer steep inclines. Avoid shifting gears under heavy load to prevent damaging the drivetrain components.

Maintaining a steady cadence
Maintaining a consistent pedaling cadence is essential for efficient climbing. Aim for a cadence of around 70 to 90 revolutions per minute (RPM) to avoid excessive strain on your muscles. Monitor your cadence and shift to a lower or higher gear accordingly to maintain a comfortable pedaling rhythm.
Techniques for efficient climbing
When climbing uphill, try to distribute your weight evenly between the handlebars and the saddle. Keep your upper body relaxed and focus on a smooth pedal stroke. Engage your core muscles to provide stability and maintain balance. Use short bursts of power when necessary, especially when overcoming obstacles or steeper sections.
Using Gears for Descending
Descending on a mountain bike requires a different gear selection approach compared to climbing. Here’s how to make the most of your gears when going downhill:
Gear selection for downhill rides
When descending, shift to higher gears to increase your speed and take advantage of gravity. Higher gears enable you to pedal less and maintain control while descending steep sections. Be cautious not to shift to excessively high gears, as it may make it challenging to maintain control or stop suddenly if required.

Maintaining control and stability
When going downhill, maintain a relaxed grip on the handlebars and allow the bike to move beneath you. Shift your body weight backward, positioning it over the rear wheel to enhance stability. Feather the brakes intermittently to control your speed and prevent the bike from gaining excessive momentum.
Tips for safe descending
Always maintain a safe distance from the rider in front of you when riding downhill. Keep your eyes focused ahead, scanning the trail for any obstacles or changes in terrain. Gradually increase your speed as you gain confidence in your bike handling skills. Practice descending techniques on moderate trails before attempting more challenging descents.
Gear Selection for Flat Terrain
When riding on flat terrain, using the appropriate gear can help you maintain speed and efficiency. Consider the following tips for selecting gears on level ground:
Finding the right gear for flat surfaces
On flat terrain, choose a gear that allows you to maintain a steady cadence without excessive effort. A gear that feels comfortable and allows for efficient pedaling is ideal. Experiment with different gear combinations to find the sweet spot that suits your riding style and fitness level.
Utilizing gear combinations
Most mountain bikes have a wide range of gear combinations. When riding on flat surfaces, you can utilize a combination of chainrings and cogs to fine-tune your gear selection. Cross-chaining, where the chain is on the extreme inner or outer chainring with the corresponding extreme rear cog, should be avoided to minimize drivetrain wear.
Maintaining speed and efficiency
To maintain speed on flat terrain, pedal consistently and avoid sudden changes in gear ratios. Focus on maintaining a smooth and efficient pedal stroke, using your gears to find the optimal balance between speed and effort. Pay attention to wind conditions and adjust your gear selection accordingly to counteract any resistance.
Proper Gear Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your gear system is crucial to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Consider the following tips for proper gear maintenance:
Cleaning and lubricating the drivetrain
Regularly clean your chain, chainrings, and cogs to remove dirt, debris, and excess lubricant. Use a brush and a biodegradable degreaser to scrub away grime. After cleaning, apply a suitable bicycle chain lubricant to ensure smooth and quiet gear shifting.
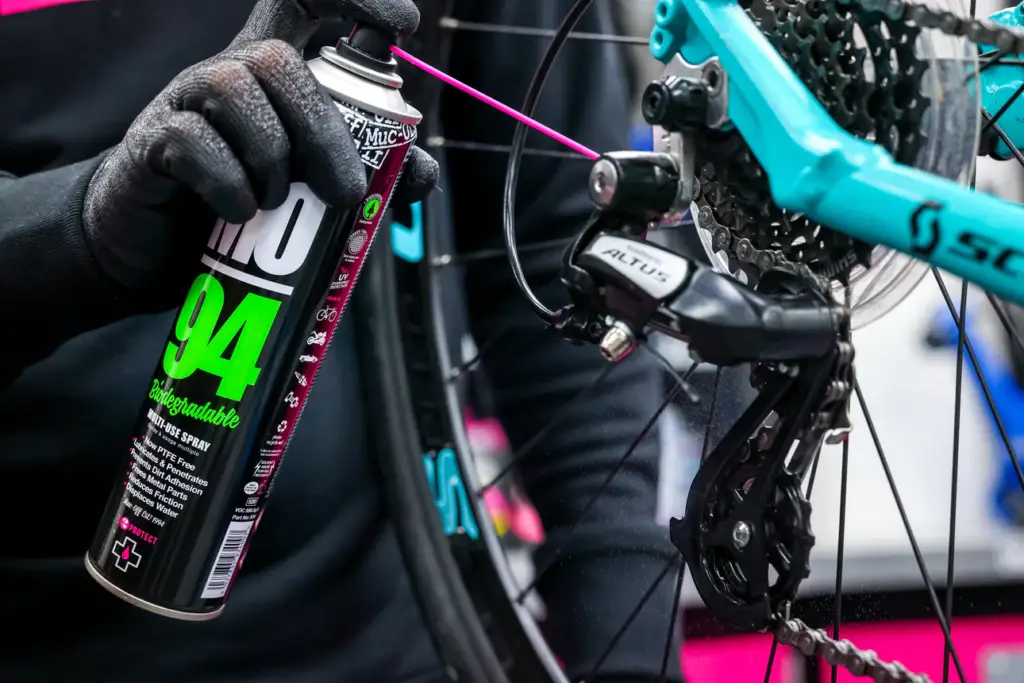

Inspecting gears for wear and tear
Periodically inspect your gears for signs of wear, such as worn-out teeth or a loose chain. A worn-out chain can cause premature wear on the chainrings and cogs, affecting gear shifting performance. If you notice significant wear, consider replacing the affected components to maintain optimal gear functionality.
Replacing worn-out components
Over time, gears may become worn or damaged. If you experience difficulty in shifting gears or notice skipping or chain slippage, it may be an indication of worn-out components. Consult a professional bike mechanic to assess the condition of your gear system and replace any worn or damaged parts.
Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a top priority when engaging in mountain biking. Here are some important safety considerations:
Wearing appropriate protective gear
Always wear a properly fitting helmet when riding a mountain bike. Additionally, consider wearing knee and elbow pads, as well as gloves, to protect yourself in case of a fall or collision. Wear clothing suitable for the weather conditions and choose shoes with good traction for better control over your bike.
Bike maintenance and safety checks
Regularly inspect your bike for any loose bolts, cracks, or damage to the frame or components. Check the tire pressure, brakes, and suspension before each ride. Make sure your bike is in good working condition to minimize the risk of accidents or mechanical failures during your ride.
Tips for safe riding in different terrains
When riding in different terrains, adjust your riding technique and gear selection accordingly. Be mindful of your surroundings, anticipate changes in terrain, and adapt your riding style to maintain control and balance. Practice good trail etiquette and respect other trail users, yielding when necessary and keeping a safe distance.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of gears on a mountain bike is a skill that can greatly enhance your riding experience. By understanding the gear system, practicing smooth gear shifting techniques, and selecting appropriate gears for different terrains, you can improve your efficiency, control, and enjoyment on the trails. Remember to prioritize safety by wearing protective gear, maintaining your bike regularly, and practicing safe riding techniques. So, gear up, hit the trails, and embark on an exciting mountain biking adventure!
Related Informative Topics :
- Best Mountain Bikes Under $500: How to Choose the Perfect Ride
- Trek Marlin 6 Vs Costco Northrock XC27 – Which Mountain Bike Truly Supreme?
- Best Upgrades Of Northrock XC27 Mountain Bike
- Northrock XC27 Detailed Review: Is it Worth the Price?
FAQs
Can I shift gears while pedaling?
Yes, it is possible to shift gears while pedaling. However, it is recommended to ease off the pedal pressure momentarily when shifting to ensure a smoother gear transition.
How many gears do mountain bikes typically have?
Mountain bikes can have various gear configurations, ranging from single-speed to 30 or more gears. The number of gears depends on the drivetrain setup and the specific type of mountain bike.
What should I do if my gears are not shifting properly?
If your gears are not shifting smoothly or skipping, it may be an indication of a misaligned derailleur or worn-out components. It is advisable to seek assistance from a professional bike mechanic to diagnose and rectify the issue.
Can I use the same gear for uphill and downhill riding?
No, the gear selection for uphill and downhill riding differs. Lower gears are typically used for climbing uphill, while higher gears are suitable for descending. Using the appropriate gear for each terrain ensures optimal pedaling efficiency.
How often should I clean and lubricate my gears?
Regular cleaning and lubrication of your gears are essential for optimal performance. Depending on riding conditions, it is recommended to clean and lubricate your gears every 100-200 miles or when they appear dirty or noisy.